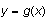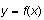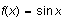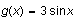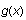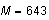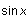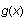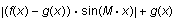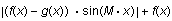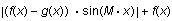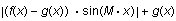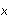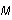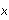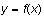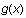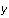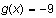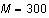|
|
Document 618
Shading regions in graphs
Version: 4.x & 5.0 - Scientific WorkPlace & Scientific
Notebook
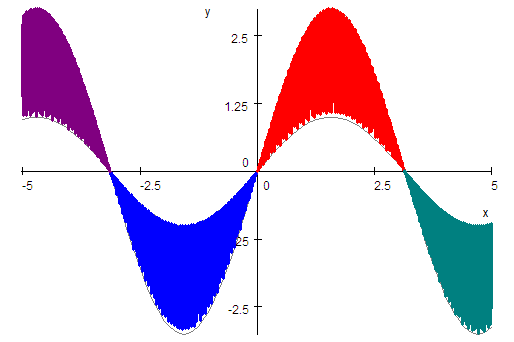
You can shade regions in SWP and SNB plots by creating quasi space-filling
curves. The method we illustrate with the first example below works on regions
where
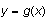 is the bottom curve. The second example illustrates shading a region below
is the bottom curve. The second example illustrates shading a region below
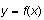 .
Adapt the methods to your needs. .
Adapt the methods to your needs.
-
From the Tools menu, choose
Computation Setup.
-
Choose Plot Behavior, select
Recompute Plot When Definitions Change, and
choose OK.
-
Define
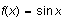 and plot the function.
and plot the function.
-
Define
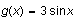 . .
-
Select
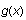 and drag it onto the plot.
and drag it onto the plot.
-
Define
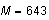 or choose some other high number.
or choose some other high number.
You may need to experiment to find an appropriate number for your needs.
-
Select the plot and choose Properties to open
the Plot Properties dialog.
-
For each expression, set the plot color and line thickness you want.
In this example, we plotted
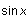 and
and
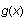 with a thin gray line.
with a thin gray line.
-
Add four new expressions to the plot:
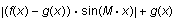
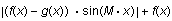
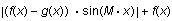
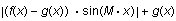
-
For the first new expression,
-
Use the Item Number box to select the
expression.
-
Set the plot color you want.
-
Set the line thickness to Thick.
-
Choose Variables and Intervals.
-
Set the
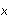 interval to -3.14 to
0.
interval to -3.14 to
0.
-
In the Points Sampled box, enter
875 or some other number greater than
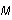 and less than 1000.
and less than 1000.
Again, you may need to experiment to find an appropriate number of samples.
-
Choose OK.
-
Repeat step 8 for the other three new expressions, setting the
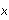 intervals to 0 to
3.14, -5 to
-3.14, and 3.14 to
5, respectively.
intervals to 0 to
3.14, -5 to
-3.14, and 3.14 to
5, respectively.
-
Choose OK.
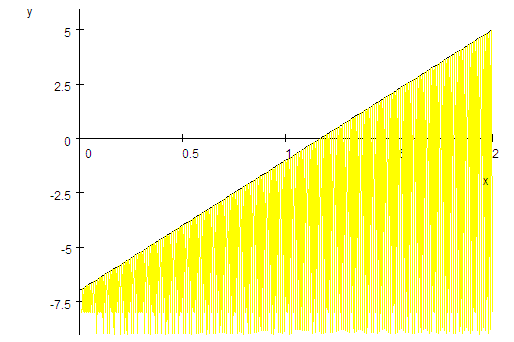
You can use the same process to shade a region below
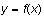 .
For .
For
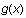 use a constant value less than the minimum value of
use a constant value less than the minimum value of
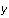 for the plot. Here we used
for the plot. Here we used
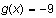 and set
and set
 . .
Last revised 07/14/07
|